Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for optimal health and well-being. There are three main omega 3s: alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). ALA, found in flaxseed, canola, soybean, and other plant oils; are essential fatty acids.¹ Similar to essential amino acids, ALA cannot be produced in the body; meaning it needs to be consumed through our diets. With sufficient intake, the body can convert ALA into EPA and DHA in very small amounts. Therefore, it is important to make sure you are getting the minimum requirements of ALA. In fact, it may be even more crucial to focus on EPA and DHA intake as some studies suggest that they provide greater benefits in regards to disease prevention..
Benefits
With roughly 60% of the brain deriving from fatty acids, it’s no surprise that omega-3s contribute to mental development, health, and function. Some of these benefits are listed below:
-
Improved mental disorder symptoms (schizophrenia and bipolar disorder)⁴ ⁵
-
Improved behavioral disorder symptoms in children (inattention, hyperactivity, impulsiveness, and aggression)⁶ ⁷
-
Prevention in mental decline associated with dementia and Alzheimer’s[⁸]
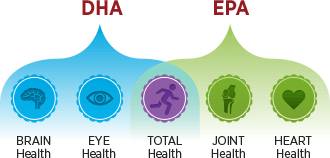 Additionally, omega-3s are associated with functions throughout the entire body. EPA is found to benefit joint and heart health, while DHA provides more benefits to brain and eye health.
Additionally, omega-3s are associated with functions throughout the entire body. EPA is found to benefit joint and heart health, while DHA provides more benefits to brain and eye health. -
Improvements in insulin resistance in those with metabolic syndrome¹³
-
Combats inflammation linked to heart disease, cancer, and rheumatoid arthritis ¹⁴ ¹⁵
-
Reductions in fatty liver in individuals with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease ¹⁶
-
Improved sleep ¹⁷
-
Joint and Skin health ¹⁸
-
Reductions in triglyceride levels, blood pressure, inflammation, and plaque
-
Improvements in ‘good’ cholesterol (HDL) levels
Recommendations
Heart disease, neonatal conditions, Alzheimer’s, diabetes mellitus, and metabolic syndrome are some of the deadliest diseases worldwide.²² All of which may be preventable through lifestyle changes, including omega-3 fatty acids. After examining the wide range of benefits through countless studies, here are the recommended intakes for omega-3s:
- The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends eating 1–2 portions of fish per week. ²³
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration recommends 1-3 g/day of combined EPA/DHA²⁴
Sources[²⁵]


- Fish and other seafood (especially cold-water fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, tuna, herring, and sardines)
- Nuts and seeds (such as flaxseed, chia seeds, and walnuts)
- Plant oils (such as flaxseed oil, soybean oil, and canola oil)
- Fortified foods (such as certain brands of eggs, yogurt, juices, milk, soy beverages, and infant formulas)
*Important to note that types of omegas found in fish have greater health benefits than those found in plants. ²⁶
Fuel Up With Fish, Defend Against Disease!
There is no denying that omega-3s are a vital part of everyday health and wellness. Loaded with benefits preventing and improving some of the deadliest diseases worldwide; omega-3s, preferably from fish, should be a part of everyone’s diet. That being said, not everyone is able to consume fish or fish oil supplements due to allergies, medications, diet specifications, or simply because of the taste. In which case, be sure to consume enough omega-3s from the plant-based sources above. Additionally, supplementation may be great and effective options for those looking for convenience, on a budget, or opposes the fishy taste. Just be careful to choose brands utilizing the proper dosage and high quality sources. Check out TimTam’s Heart + Joint for a quality fish oil supplement that you can trust!


